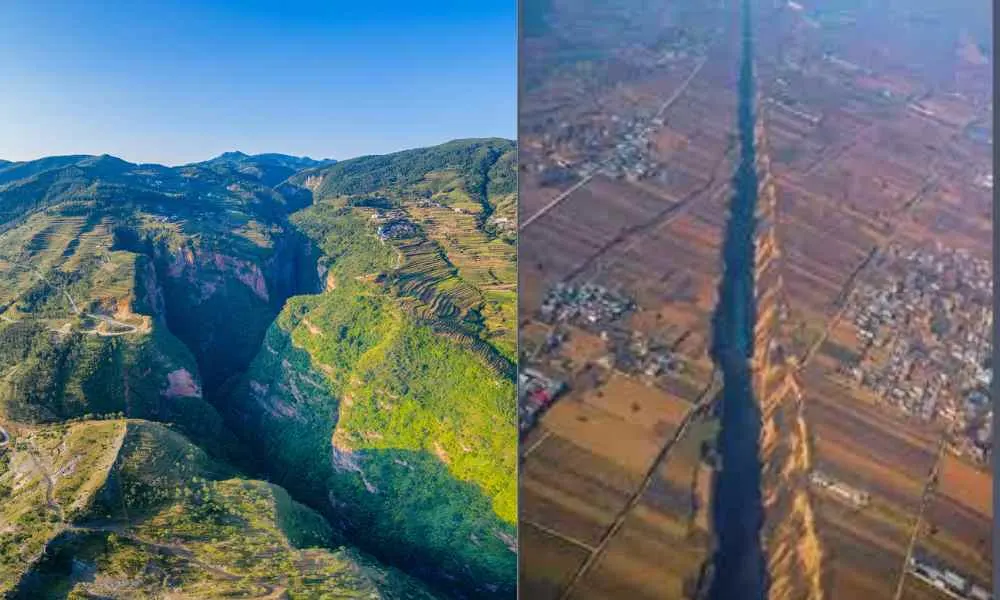
Rift valleys are remarkable geological features that stretch across the Earth’s surface. Characterized by their linear shape, deep depressions, and steep sides, these valleys mark the sites where tectonic plates are steadily drifting apart. The shifting exposes a cross-section of the Earth’s crust. These range in scale from vast rifts like the iconic Great Rift Valley. The Great Rift extends thousands of kilometers in Eastern Africa. There are also smaller yet significant formations in various locations around the globe.
Their formation involves a region of the lithosphere that undergoes extensional stress. This leads to the splitting and thinning of the crust. Over time, as these plates continue to divide, they create rift valleys. They may further grow into oceanic ridges or even form new seas.
Formation of Rift Valleys
These valleys are significant geological formations created by the movement and interaction of tectonic plates.
Tectonic Plate Movement
Tectonic plates, the vast rigid sections of the Earth’s lithosphere, are constantly moving atop the semi-fluid asthenosphere. When two plates move apart, tensional forces create fractures in the Earth’s crust. Over time, these cracks can lead to the formation of a rift valley.
Through a process known as rifting, these splits cause the crust to thin and stretch. Sometimes over many millions of years, the surface drops in to form a lowland region. As the plates continue to separate, narrow valleys evolve into broader valleys. These span for hundreds of kilometers in width and can also extend along thousands of kilometers.
Volcanic Activity
In addition to tectonic movements, volcanic activity is naturally linked with the development of rift valleys. In these regions, the thinning crust may allow magma to rise more easily towards the surface. This molten rock can erupt as lava. Over time, rift valleys may become sites of frequent volcanic eruptions.
As the rift valley widens and the volcanic activity continues, increased sedimentation and volcanic deposits can further shape the valley. Volcanoes and other features along the rift, such as hot springs and geysers, are common due to the presence of heat beneath the rifted crust. These processes play a defining role in the development of rift valleys.

Characteristics of Rift Valleys
Rift valleys are special geological formations that display telling features of the tectonic forces that shape them.
Steep-Sided Walls
The walls of these valleys are typically very steep, rising dramatically from the valley floor. This is a result of the earth’s crust being pulled apart, leading to the sinking of land between large faults. These vertical walls can sometimes form in a series of steps and terraces with contrasting movements along the fault lines.
Flat Valley Floors
Central to rift valleys is their flat valley floors. These flats are a result of the region sinking uniformly between parallel faults. This sinking creates an extensive flat surface that is often below sea level. In some locations, the floors of rift valleys are occupied by long, narrow lakes.
Elevated Shoulders
Rift valleys are frequently flanked by elevated shoulders, which are higher grounds that form the borders of the trough. They result from the tilting of adjacent blocks of the earth’s crust along the fault lines. These raised areas can also give rise to unique ecosystems due to their various climates and altitudes.

Major Rift Valleys of the World
Rift valleys represent significant geological formations created by tectonic activity. Here, we highlight some of the most notable rift valleys across the globe:
The East African Rift Systems (EARS)
This rift stretches from the Afar Triple Junction in northeastern Africa down through eastern Africa. This system is home to remarkable features such as Mount Kilimanjaro and Lake Victoria and is gradually splitting the African Plate into two separate plates.
Formed between 22 and 25 million years ago during the Miocene epoch, the EARS is the result of tectonic plate movements that are pulling the African continent apart. Geological forces within this system continue to shape the landscape, new geological formations, and the potential creation of a new ocean basin as the Somali Plate and Nubian Plate drift apart.

The Baikal Rift Zone
The valley in Siberia is home to Lake Baikal, the world’s deepest freshwater lake. This rift is unique because it is located in a region typically associated with continental collision rather than rifting.
The Baikal Rift Valley is a profound geographic feature situated in southeastern Russia, beneath the surface of Lake Baikal. This valley is the result of significant tectonic activity, where the Eurasian and Amur Plates are moving apart, shaping a network of rifts that characterize the zone. These rifts have generated a landscape marked by a series of basins that stretch over 2,000 kilometers.

The Great Rift Valley
The rift encompasses the Jordan River Valley part of the larger East African Rift, which includes the Dead Sea, the lowest point on the Earth’s land surface.
Spanning approximately 6,000 kilometers, it extends from Lebanon’s Beqaa Valley in Asia to Mozambique in Southeastern Africa. Within the Great Rift Valley, one can find complex fault lines such as the Eastern Rift and the Western Rift. These include some of the world’s deepest lakes, like Lake Tanganyika. The valley’s floor is a hub of volcanic activity, housing multiple active and dormant volcanoes.

Shanxi Rift System
The Shanxi Rift System, located in northern China, is a significant geological formation that forms part of the larger Taihang Mountain Range. This rift system is characterized by a series of parallel rift valleys that have been created by the extensional tectonic forces acting in this region. The formation of these valleys is primarily attributed to the East Asia Rift System. The Shanxi Rift System spans a length of approximately 800 kilometers, showcasing a remarkable example of rift valley formation.
One of the most notable things about the Shanxi Rift System is its impact on the region’s geography and biodiversity. The valleys within this system vary in width, ranging from a few kilometers to over 50 kilometers wide. They are also flanked by steep cliffs and mountains, some of which reach heights of over 2500 meters.

The West Antarctic Rift
This system is a major rift valley lying beneath the vast ice sheets of Antarctica. It has been explored through seismic studies and ice-penetrating radar.

The Rio Grande Rift
The massive rift in North America extends from Colorado down to Chihuahua, Mexico. It is evidenced by the notably high volcanic activity along its length.
Location & Geographical Impact:
- Northward Extension: Begins in central Colorado.
- Southward Extension: Reaches down to Chihuahua, Mexico.
- Formation: Due to the pulling away of the Colorado Plateau from the High Plains.
Geological Features: - Basins: Lowland areas formed between ranges.
Ranges: Elevated areas are often home to dramatic landscapes.

The Rhine Rift Valley
The Rhine rift in Europe cuts through Germany and forms a significant part of the European Cenozoic Rift System. The Black Forest and the Vosges Mountains are part of this valley.

The Red Sea Rift
The Red Sea Rift is a sea that was created by the divergence of the African and Arabian Plates, showcasing a young but well-defined rift valley.

Ecological and Geological Significance
Rift valleys are notable for their unique ecosystems. They offer a variety of habitats, which range from dry deserts to lush forests. This diversity enables them to support a wide array of wildlife species, including some that are endemic and thus critically important for biodiversity.
For example, the Great Rift Valley stretches from Syria to Mozambique and houses numerous protected areas and national parks, becoming a sanctuary for threatened species.
From a geological view, rift valleys serve as live windows into Earth’s ongoing tectonic movements. These regions are forming where the planet’s tectonic plates move apart. They show the process of seafloor spreading at the bottom of the oceans. Geologists study the rifts to understand geological history and earthquake potential. These areas often have seismic activity due to the presence of fault lines.
Conclusion
Rift valleys serve as a vivid testament to Earth’s dynamic nature, forming when tectonic plates diverge and giving rise to unique geographical features. From the extensive East African Rift, a beacon of natural beauty and geological wonder, to the submarine rifts that give evidence of seafloor spreading, such as those detailed by the National Geographic Society, they have been the subject of keen scientific interest and fascination.
These formations reflect not only the immense forces at work beneath our feet but also the evolutionary journey of continents. The process of rifting impacts ecosystems and climates, and it plays a critical role in the biodiversity of our planet.
Also read,