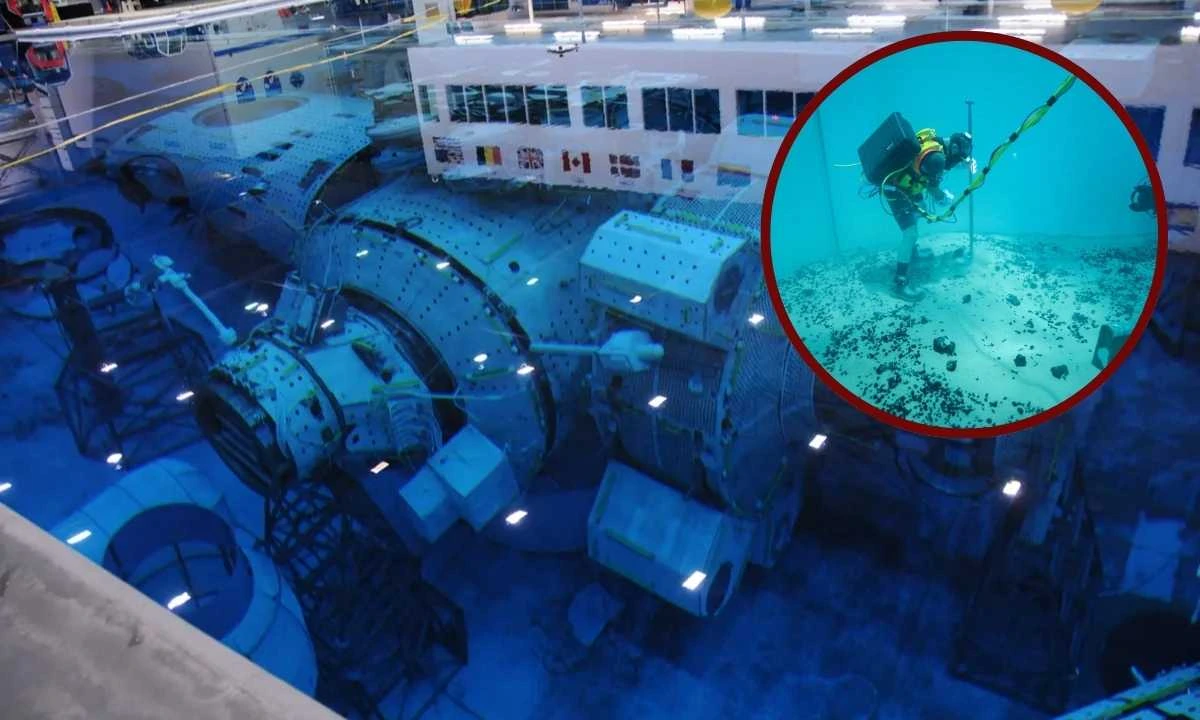
Imagine preparing for the weightlessness of space while still on Earth. That’s precisely what NASA astronauts do at the Neutral Buoyancy Laboratory (NBL). This world-class facility near Houston, Texas, is home to one of the largest indoor pools on the planet. It plays an important role in astronaut training by simulating the conditions of microgravity found in space.
The NBL is much more than a pool; it’s a cornerstone for mission success. By creating a neutral buoyancy environment, astronauts can experience the challenges of spacewalks, known as Extravehicular Activities (EVAs), before heading into orbit. Let’s have a closer look at how it functions and how the astronauts take the 40-foot dive.
Key Features of the Facility
The NBL’s pool is massive. Measuring 202 feet long, 102 feet wide, and 40 feet deep, it holds 6.2 million gallons of chlorinated fresh water. The temperature is carefully maintained between 84°-86°F. It ensures a comfortable environment for divers and astronauts alike.
Inside the pool, full-scale mockups of International Space Station (ISS) modules and visiting spacecraft, like SpaceX’s Dragon and JAXA’s HTV, provide realistic training settings. Past features, such as the Hubble Space Telescope mockup and Space Shuttle payload bay, were removed once they were no longer needed.
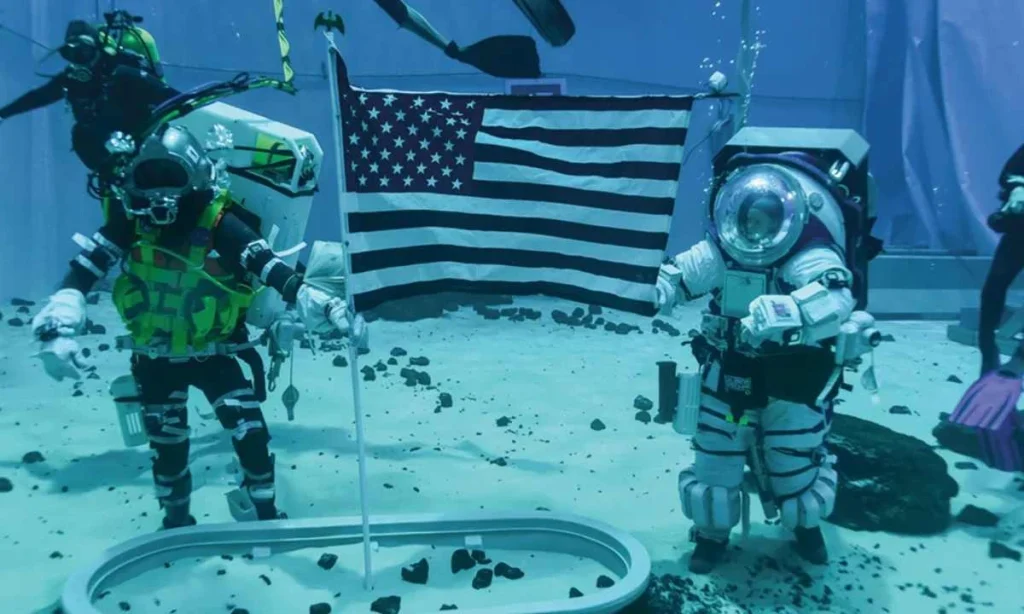

Why NBL is Vital
The NBL isn’t just a training ground. It’s a critical tool for space mission success. Astronauts use the facility for mission planning, hardware verification, and refining procedures for time-critical EVAs. These tasks demand precision and familiarity, and the NBL allows astronauts to practice them repeatedly in a controlled environment.
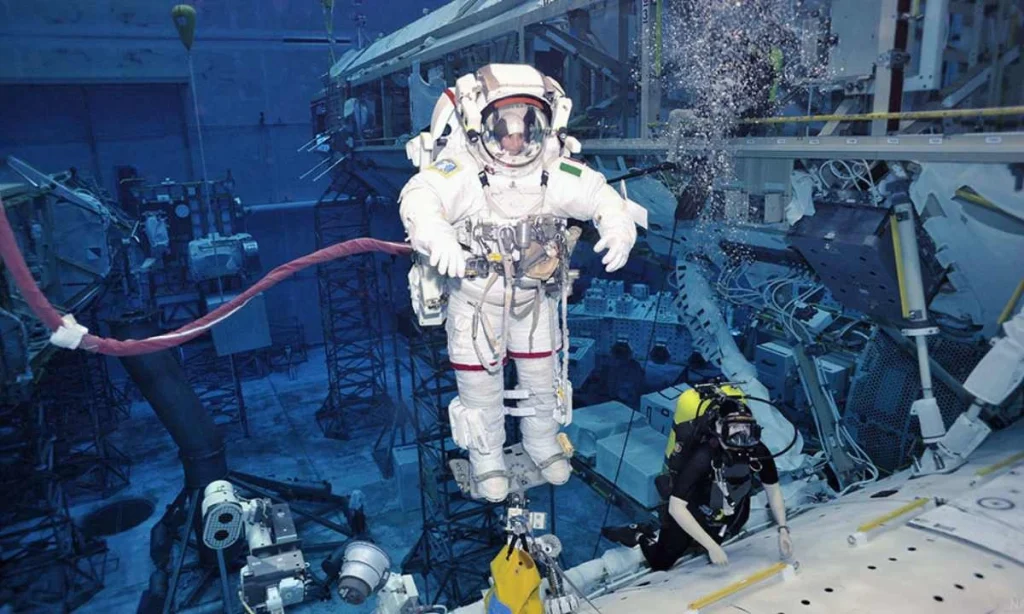

NBL simulates the weightlessness of space and it ensures astronauts are well-prepared to handle the challenges of spacewalks. As NASA puts it, this training is essential for “refining time-critical operations necessary to ensure mission success.”
Inside the Neutral Buoyancy Laboratory
Facilities and Technology
The NBL is packed with state-of-the-art technology:
- Integrated control rooms oversee mission simulations.
- Advanced video, audio, and instrumentation systems track every movement.
- Multiple crane systems help handle heavy equipment.
- A hyperbaric chamber treats dive-related emergencies, while an altitude chamber simulates the physiological effects of flying.
Mockup Logistics and Repairs
The Logistics and Mockup Facility (LMF) is a hub of activity. It includes workshops for mockup fabrication, repairs, and maintenance. Specialists use techniques like welding, sewing, and woodworking to create and modify equipment used in training.
Diver Support and Safety
A team of certified professional divers provides operational support. Using SCUBA and surface-supplied dive systems, they ensure safety during underwater simulations. Nitrox and air systems are available, along with an on-site hyperbaric chamber for emergencies.
History of Neutral Buoyancy Training
NASA’s journey to the NBL began in the late 1980s. The previous training facility, the Weightless Environment Training Facility (WETF), was effective but too small for the larger ISS mockups needed for future missions.
In the 1990s, NASA purchased a structure from McDonnell Douglas and retrofitted it into what we now know as the NBL. Originally, plans called for a larger pool, but to save costs, its dimensions were downsized to 202 feet by 102 feet, with a depth of 40 feet. This strategic decision allowed NASA to create a state-of-the-art training center without breaking the budget.
Astronaut Training at the NBL
Spacewalk Preparation
The NBL provides a unique environment where astronauts can simulate weightlessness. By using neutral buoyancy suits, they practice handling tools and maneuvering in conditions that mimic space.
Time-Critical Missions
The NBL is essential for refining emergency procedures during spacewalks. Astronauts rehearse responses to unexpected challenges, ensuring they’re prepared for the high stakes of orbit.
Mental and Physical Conditioning
Training at the NBL also helps astronauts adapt to the stress and demands of space missions. The realistic environment builds confidence and familiarity, making their tasks in orbit more manageable.
The Environmental and Scientific Perspective
Engineering Feats
The NBL is a marvel of engineering. It combines innovative technology with sustainable practices to create a controlled environment that closely mimics space conditions.
Conservation and Water Usage
Maintaining a pool of this size requires careful resource management. NASA uses chlorinated fresh water and follows strict conservation practices to minimize environmental impact.
Conclusion
The Neutral Buoyancy Laboratory is more than just a training pool—it’s a testament to human ingenuity and the relentless pursuit of exploration. From simulating microgravity to refining mission-critical procedures, the NBL ensures that astronauts are ready for the challenges of space.
This incredible facility reminds us of the lengths humanity will go to in its quest for knowledge and exploration. For those curious about space and the technologies that make exploration possible, the NBL stands as a shining example of innovation.
Also read,