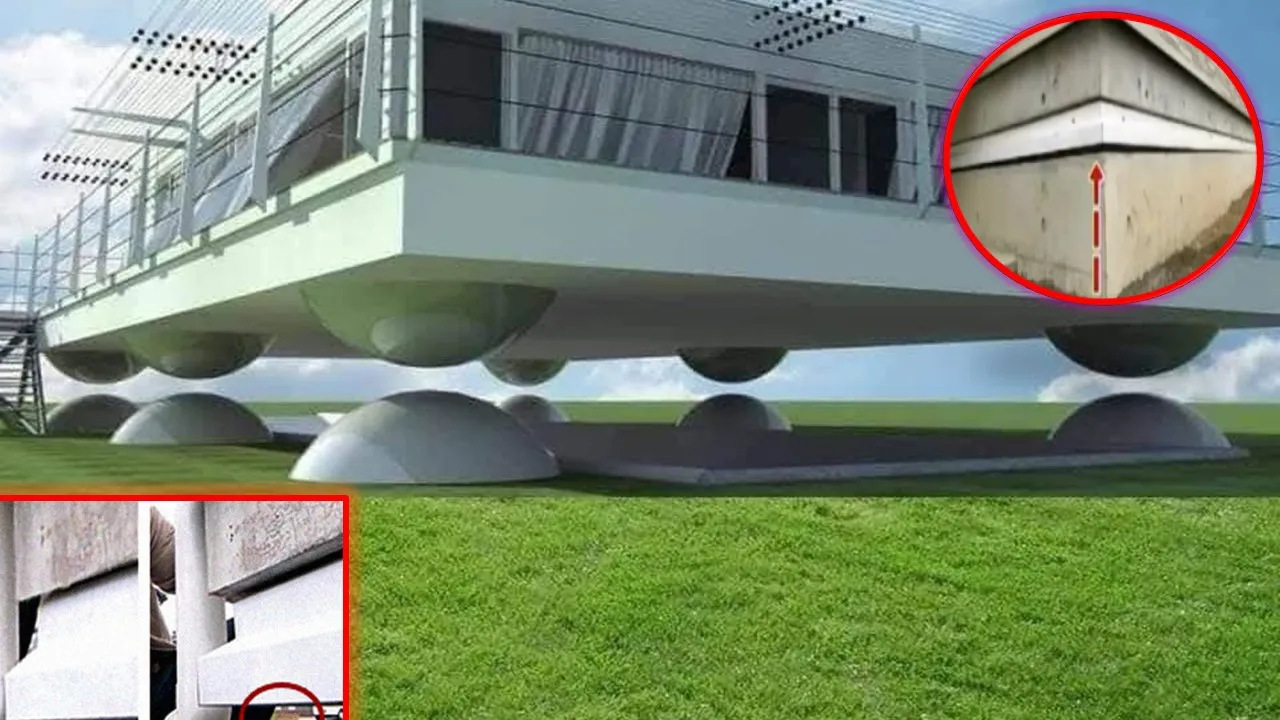
Japan is one country that encounters many tremors around the clock. Engineers from Japan have come up with a unique offering that is going to see houses float above ground. This technology of levitating houses by the Japanese company Air Danshin protects houses from destruction during an earthquake. As per the design, the house sits stable on a deflated airbag which will be compressed with air once its sensors feel tremors from the ground. Let’s look into how this technology works, its applications, and the impact it can have on future construction practices.
Technology Behind Houses Floating In The Air
The floating house system is one of the creations by Japanese engineers who used compressed air to raise houses away from their foundations during an earthquake. It works immediately when earthquake tremors begin because it forms a compressed air base under the building. The one-foot-thick floating base on which it sits allows its three centimeters (1.2 inches) to rise free from vertical movements, simulating houses floating in the air and minimizing chances for likely structural damage.
Technology makes it work massively within a short time period such that whenever an earthquake hits, the house is always stable. More than 100 homes in Japan already adopted this system. Sources say that most of the houses have maintained their integrity despite heavy tremors. As a result of its effectiveness, there is now interest in using this technology to safeguard other classes of buildings like hospitals and schools as well, possibly incorporating houses floating in the air.
How the Airlift System Works
The way an Airlift System works is that it has a seismic sensing device that activates the moment the earthquake starts. Air Danshin Systems Incorporated invented this system, which releases compressed air from tanks located below the house. The resulting air forms a cushion that raises the entire structure slightly above ground, thus enabling it to “float” on a cushion of air. This kind of movement resembles houses floating in the air, where seismic wave force is minimal, leading to the protection of both the building’s structure and its materials.


This tech operates very effectively and needs very little upkeep. The airlift systems are therefore the best choice for earthquake-prone areas as they have an easy maintenance procedure. The system’s design is such that it is simply installed in existing houses which would allow for wider adoption and potentially build houses that give the impression of floating in the air. This increases Earthquake resistance in urban residential areas.
Applications and Success Stories
Japan has undoubtedly adopted this airlift technology in various kinds of buildings, including both single-family and bigger commercial constructions. Such is the case for at least 88 houses built to withstand earthquakes in Tokyo, an area known for its seismic activities. House owners say that their homes stayed intact even after experiencing strong shakes, effectively showing the practical application of houses floating in the air during seismic events.
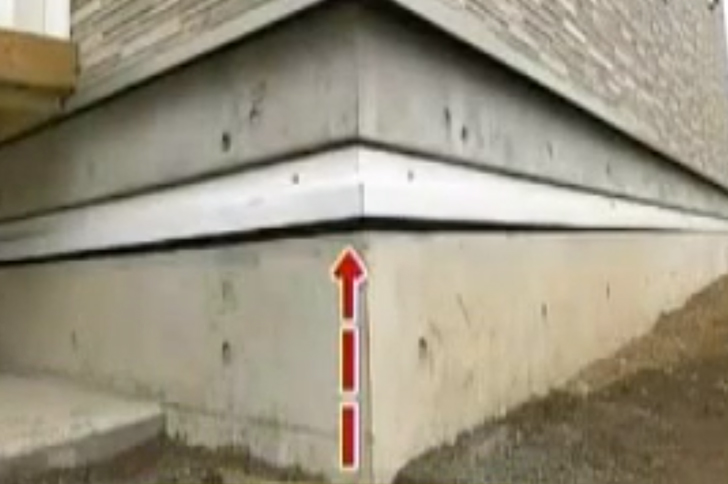


Also, this technology has been adopted in several critical infrastructures other than residential homes. That is for instance hospitals, emergency response centers etc. It is essential that these places are functional during and after an earthquake turmoil; thus, the lift provides the security needed. This technology’s success in these sectors supports its ability to save lives. It will also reduce financial burdens associated with quakes, further promoting the idea of houses floating in the air as a feasible solution.
“You design buildings to protect people’s lives. That’s the minimum requirement”
Ziggy Lubkowski, a seismic specialist at University College London.
Houses Floating In The Air: Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite its benefits, floating house technology has some challenges. The first thing that comes into mind when discussing this issue is the cost of these houses. They can vary from $20,000 to $70,000 depending on their size. In addition, routine inspections are necessary for the system to be able to operate well, hence increasing maintenance expenditure. However, the potential benefits of having houses that seem like they are floating in the air outweigh these challenges.
This is an attractive choice for earthquake-prone areas despite the difficulties. Japan’s use of this technology sets an example that other seismic risk countries can follow. Higher acceptance rates will probably encourage more regions to embrace this technology in order to protect their citizens from danger, and potentially imagine a future where houses floating in the air become a common sight.
As we look ahead into the future, researchers still find ways of improving this technology. It is by making it cheaper and more accessible. Innovations such as integrating the airlift system with other earthquake-resistant technologies could improve its effectiveness. Research will continue further in this direction. As a result, floating houses can be built around the globe as a common feature in earthquake-resistant construction, possibly giving rise to the era of houses floating in the air and ensuring that people living in high-risk areas are safe.
The Broader Impact on Earthquake Safety
The advancement of floating huts stands for a considerable progression in quake-proof. This technology saves lives and protects properties by diminishing the influx of seismic waves against edifices. It also assures tranquility to residents living in areas with frequent earthquakes. That is because they know that they have new technological advances within their houses to protect them. One significant advancement is the idea that these houses could seem like they are floating in the air during an earthquake.
In the course of its preparedness for disasters, Japan is developing new technologies and concepts. They are widely used in these types of programs. This means that floating houses are one of those that measure up. With the discovery of unprecedented technological feasibility and safety measures, construction in earthquake-prone areas around the world can become a reality, making it a dream come true for many. In the future, we might see more houses floating in the air due to these technological advancements.
Conclusion
In the case of Japan, there are earthquake-resistant houses, which have become a notable advancement in disaster management. Therefore, this technology provides a solution to pressing issues. It also ensures enhanced security for regions that experience seismic activities such as earthquakes. When more and more people adopt it globally, it can change construction safety in seismically active areas permanently. That is, homes and infrastructure will be better prepared against natural dangers, potentially creating a world where we have houses floating in the air.
Also read,